The Single Strategy To Use For Local News Online
Wiki Article
An Unbiased View of Local News Online
Table of ContentsThe Basic Principles Of Local News Online The smart Trick of Local News Online That Nobody is Talking AboutThe 5-Minute Rule for Local News OnlineThe Local News Online IdeasWhat Does Local News Online Mean?Not known Factual Statements About Local News Online
Every year we pay out billions of dollars directly to the publishing partners in our ad network. We pay participating news publishers to curate and allow users access to select paywall articles for , an online experience that’s powered by a $1 billion investment in news organizations. As of June 2023, more than 2,300 publications globally are part of News Showcase and we’ve launched the product in 22 countries.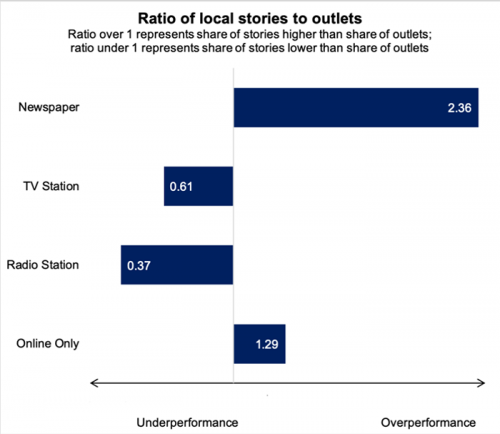
Not much has changed about the economics of local news. It’s still a slog. But executives in the space say they see an opportunity — and an audience begging for news. “The only route that we could see for local to work would be to go in relatively small with clear-eyed expectations and then only build up as your presence, readership and revenue builds up,” said Axios CEO Jim Vande, Hei.
But the opportunity is to make small, targeted investments geared towards fast profitability (and eventually group multiple cities together to better sell to advertisers). If the system works, “We’ll know fast,” Vande, Hei added. For years, the conversation about local news has been almost entirely a dismal one. Regional newspapers have been the hardest hit by the changing economics of the news business, first the switch from print to digital and then the rise of Facebook and Google and the deterioration of the online advertising market.
See This Report about Local News Online
Plotz said that coronavirus crisis had also diluted the concentration of media talent in major cities like New York and Washington, as some people move to other locations and work online. He believes that could help him find hosts — and the local news ecosystem in general. “There’s a recognition that people can be more distributed, and that may make one of the challenges of doing local things slightly easier to overcome,” he said.For years, public radio stations were dependent on NPR to provide their most valuable contentassets. But as listenership has migrated to digital, radio stations have branched out to make more of their own original programming. In 2018, for instance, local news sites Gothamist, LAist, and DCist were taken over by local radio stations WNYC, KPCC, and WAMU, respectively.
Evan Smith, the CEO of the Texas Tribune, said that when launching the local politics driven news site more than a decade ago, “We decided that for-profit was a non starter and that the market had failed.” Smith said the Tribune’s public service mission meant that its content had to be free.
More About Local News Online
A mix of donations, reader revenue, and events (in the before times) has made Texas Tribune one of the most recognized non-profit newsrooms in the country. Smith said he still believes for-profit ventures in local news are exceedingly difficult. “I’m for anybody who solves this problem,” he said. “It’s for for-profit or non-profit, God bless, as long as the problem gets solved.” .Knight Foundation. About two-thirds of the residents in each city discuss local news in person a few times a week or more. During a period of tremendous technological change—change that is far from complete—this study takes a microscope to the information streams in three news environments across the United States: —a highly educated urban area of more than 2 million with internet adoption above the national average and a large Hispanic population (19%); —a metro area of 175,000 with a substantial share of black residents (41%), an unemployment rate above the national average, and a local university working to serve as a hub for journalism innovation; and —a city that spans three states and has a predominantly white population of just 125,000.
cities is in terms of volume and choice, the former of which may well have an impact on the latter. Denver’s 140+ identified news providers—including 25 digital-only outlets—is about 2. 5 times that of Macon (24) and Sioux City (31) combined. And that seems to have some impact on the dominance of legacy providers in each city.
you can look here
The Buzz on Local News Online
In all three cities, the portion of residents who often get local news from neighborhood associations, government agencies or officials, or digital-only outlets is in the single digits. Local News Online. The study also suggests that some populations are more engaged with their local news stream, and that this holds across a broader range of topicsNine out of 12 topics covered—from weather to education to the local economy—are closely followed by at least 20% of Macon residents, while that is true of just six topics in Denver and five in Sioux City. This higher rate of interest from Macon residents exists in civic-oriented great post to read topics such as education and government as well as local crime.
Facts About Local News Online Uncovered
Only six of the 24 news providers in Macon and seven of the 31 identified in Sioux City offered daily digital content. Among just the digital only outlets in Denver, there were more offering daily content – 11 of the 25 (Local News Online). Denver news providers also demonstrate a greater use of digital opportunitiesAmong the other major findings: Both Hispanics in Denver and blacks in Macon closely follow local and neighborhood news at higher rates than their white counterparts. In Denver, 60% of Hispanics compared with 43% of whites closely follow news about the local area. In Macon that is true of 70% of blacks compared with 43% of whites.
14% of whites). Denver and Learn More Here Macon differ in at least one major way when it comes to news sources targeted toward these populations: Researchers identified nine outlets in Denver aimed at Hispanics and/or Spanish speakers (Local News Online). In Macon, researchers found just one that appeared to cater directly to the black community
Little Known Questions About Local News Online.
Combined, they produce more than 25 hours of news each weekday – and at this point, on-air programming is far more of a draw than TV websites. The study of five days of content in each city finds that routine traffic, weather and sports segments accounted for about a third of the airtime.The reliance on anchor reads plays out in the length of stories, though the averages here did vary by city. Nearly half, 45% of non-sports, weather and traffic stories on Denver stations were 30 seconds or shorter, compared with 29% in Sioux City and 17% in Macon. Fewer than two-in-ten stories in each city were more than two minutes long.

Report this wiki page